Purpose
With openfile(), you can open a file to either read or write the data into it. The output option in the command will create a new file with the specified file name in your scripts folder. If a file with that name already exists in the folder, then the command will replace it with the new one.
The openfile() returns a boolean value based on the open status of the file.
- True: If the file opened successfully
- False: If the file is not opened
Syntax
Format 1: Opens a file existing in your SAP work directory.
openfile("filename",{"options":"value"});
Note: If a file path is not specified, the file will be created in the SAP work directory on your local system. Supported file types are .csv, .txt, and .xls.
Format 2: Opens a file existing in the specified location on your system.
// You need to place double backward slashes between the folder names in the file path. openfile("C:\\LiquidUI\\MMModule\\filename.ext",{"options":"value"});

Note: You need to specify the file path in the command if the file does not exist in your scripts folder.
Properties
- filename - filename to enter data
- delimiter - delimiters to separate data
Options
The openfile command takes the following options:
|
"append": true - If true, the append option allows you to append or write to a file. "append": false - If false, you cannot append or write to a file. |
|
|
"delimiter": value - The delimiter option identifies the character used to separate between data entries in a file. |
|
|
"output": true - The output option will create a file with the specified file name. If the file already exists, it will be deleted and replaced with a new empty file. |
Options Detail
Example
The following scenario demonstrates the openfile() command usage:
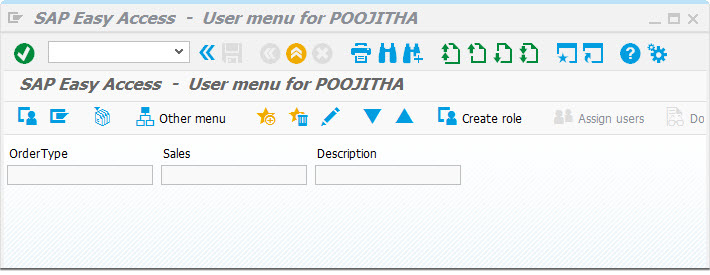
On the SAP Easy Access screen, create 3 fields with the labels:
- Order Type
- Sales
- Description
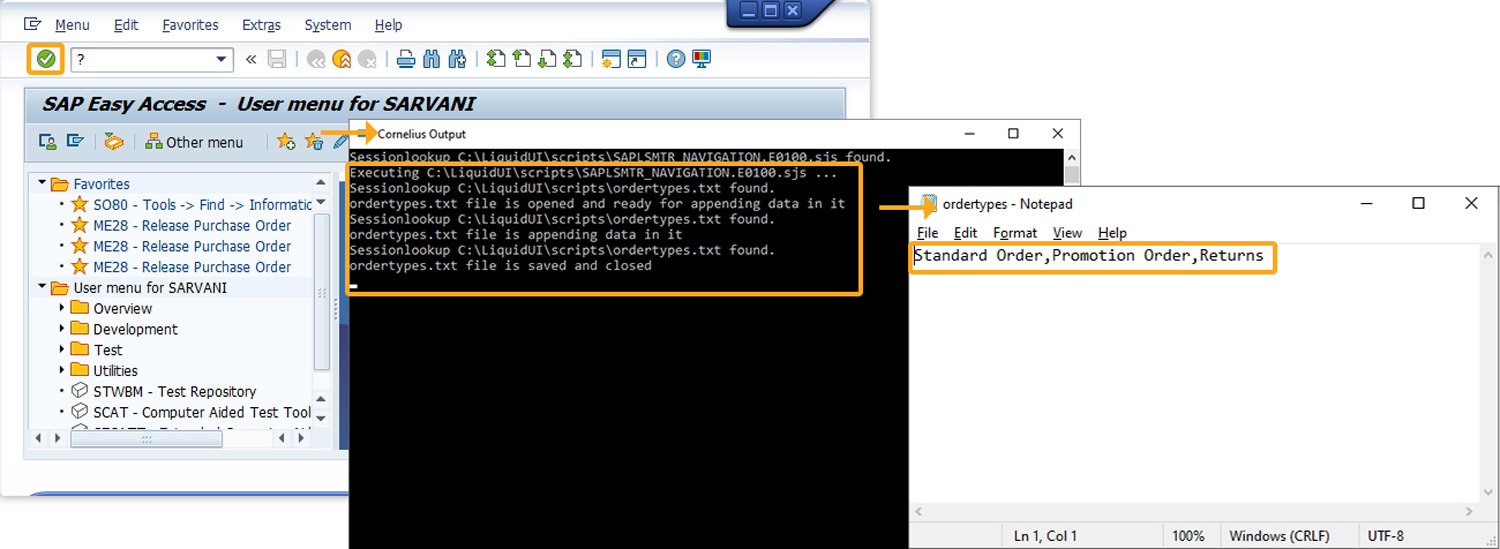
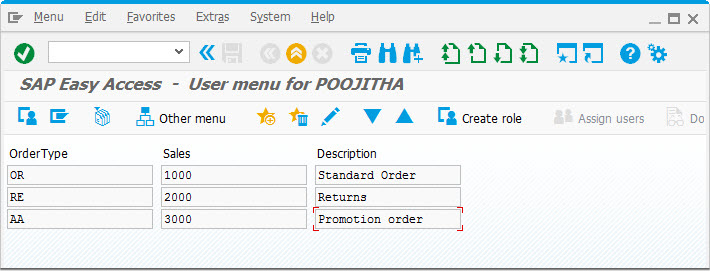
Create a file with the following data:
OR,1000,Standard Order
RE,2000,Returns
AA,3000,Promotion order
Create a script file using the script provided on the Script Details page and save the file.
The SAP Easy Access screen appears, as shown below:
Press Enter key. The data from the file appears in the fields, as shown below:
Script Details
openfile('file1.txt',{"delimiter":","});
Tips and Tricks
-
It is not required to open a file explicitly with openfile() since readfile() or appendfile() contain an implicit open. But a missing closefile() means that a readfile() will read nothing at all for the next time.
-
File Handling
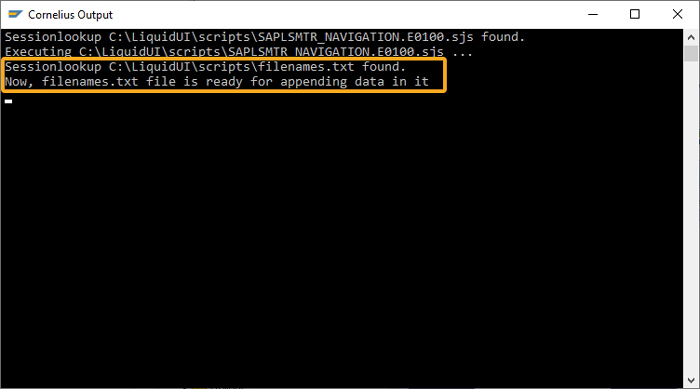
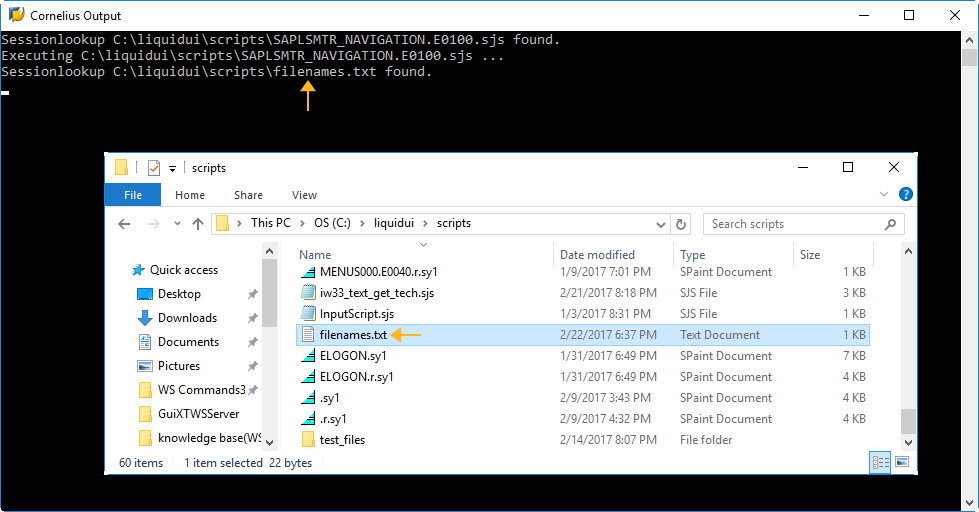
This example shows you how to open a file, append data, and then close the file. Here we used .txt file, however, you can use .csv and .xls as well.
openfile("filenames.txt",{"delimiter":";","output":true}); appendfile("filenames.txt",{"name1":true,"name2":true,"name3":true}); closefile("filenames.txt");Learn more about the File Handling example.
-
In each SAP mode, it is valid to open and close files separately.